Coronary Angioplasty
Coronary Angioplasty
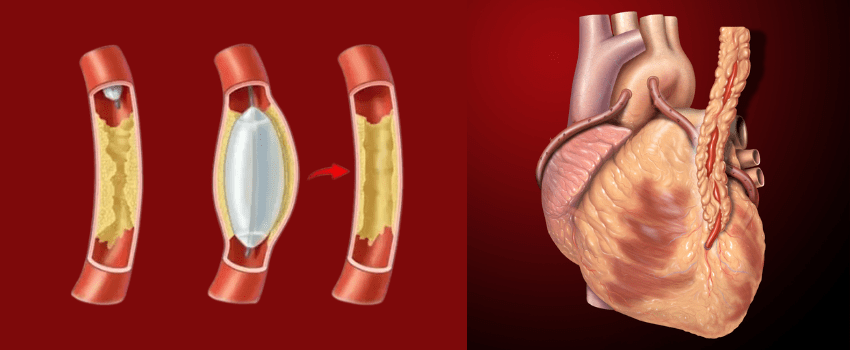
Unblocking and restoring blood flow
Coronary angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure used to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. A small balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a metallic or drug-eluting stent is often placed to keep it open and ensure optimal blood flow to the heart.
Why this procedure is important
- Restore blood flow in a blocked artery.
- Relieve symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Prevent serious complications such as heart attacks.
How the procedure is performed
- Preparation: The patient is informed and usually fasts. Local anesthesia is applied, and medications are adjusted before the procedure.
- Access: The cardiologist inserts a catheter through the radial (arm) or femoral (groin) artery and guides it to the affected coronary artery.
- Dilation: A balloon is inflated to open the vessel, followed by placement of a stent if needed.
- Final check: Blood flow is verified using contrast dye and imaging.
- Duration: Usually 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on complexity.
- Aftercare: The patient is monitored closely and receives instructions for gradual recovery.
Safety and effectiveness
Coronary angioplasty is performed in a highly secure environment with continuous monitoring by a specialized team. Complications are rare, and the procedure is considered safe when performed by an experienced cardiologist.
Our approach
Angioplasty is carried out with individualized care. Patients are fully informed before the procedure, guided throughout, and carefully monitored afterward. Results are explained clearly, and personalized follow-up ensures optimal recovery and long-term prevention.